This recent study found that over half of children and young people with Cerebral Palsy have more than one movement disorder, which is more common than previously thought.
Dr. Heather Riordan explains how different motor types can occur at the same time in some people and how to decide what to treat first.

Neurologist and movement disorder specialist, Heather Riordan, MD, describes the Chorea in Cerebral Palsy and what to do if it is impacting your function.

Do you or your child have movements that are difficult to control? Is your mobility and function impacted by abnormal movements or do these movements cause pain? If so, you or your child may have Dyskinesia. If you want to learn more, including how it is treated, don't miss this educational Town Hall with experts Dr. Heather Riordan, from Kennedy Krieger Institute, and Dr. Michael Kruer, from Phoenix Children's.

CPF Executive Director Rachel Byrne and Dr. Heather Riordan, Director of the Phelps Center for Cerebral Palsy at the Kennedy Krieger Institute discuss dyskinesia.

The Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy Functional Impact Scale is a new tool useful measuring the functional impact of dyskinesia on children's movements and postures and the perceived impact of dyskinesia on daily activities. It can can help identify priorities for intervention.
This systematic review looks at all available evidence for pharmacological/neurosurgical interventions for managing dystonia in individuals with cerebral palsy to inform the AACPDM care pathway.
Hypotonic CP, also known as hypotonia, is a form of cerebral palsy that causes low muscle tone. In other words, the muscles are overly relaxed and your child may feel floppy.

Mixed types of CP refer to symptoms that don’t correspond to any single type of CP but are a mix of types. For example, a child with mixed CP may have some muscles that are too tight and others that are too relaxed.

Ataxia affects balance and depth perception. Children with ataxia will often have poor coordination and walk unsteadily with a wide-based gait.

Dyskinesia is an umbrella term encompassing a range of different movements. These are all movements that can be out of your control. Dyskinesia is very common in cerebral palsy.

Dr. Bhooma Aravamuthan presents Understanding Dystonia: Diagnosis and Treatment at the 2020 AACPDM Community Forum. Moderated by Council Chair, Jen Lyman.
The Dystonia Care Pathway was updated in 2024 based on best available evidence. The goal of the these Care Pathways is to help Health Care Professionals understand the research evidence on the topic so that they can make clinical decisions for the care of the individual.
Spastic cerebral palsy is the most common type of CP. People will experience increased muscle tone and their movements may appear stiff or awkward.

People who have dyskinetic cerebral palsy experience involuntary movements that are difficult to control. These movements can be slow, twisting and writhing, or rapid and jerky, and can impact movement in the hands, arms, feet, legs and even the face or tongue.

Do you or your child have movements that are difficult to control? Is your mobility and function impacted by abnormal movements and cause pain? If so, you or your child may have Dyskinesia. If you want to learn more, including how it is treated, please join us on for a new educational Town Hall with experts Dr. Susan Biffl, from Rady Children's Hospital, and Dr. Mark Gormley, from Gillette Children's.

My boys were exactly the same amazing, lovable, adorable, brilliant little boys after the diagnosis, that they had been before it. The exact same.

The typical cognitive assessments that are used for children require them to be able to use their hands to point to pictures or hold puzzle pieces.

"Cerebral palsy is primarily a motor impairment so it's really important to look at what the child’s motor function is. Are they developing on the trajectory of a child who has cerebral palsy or are they developing as we would expect a baby to develop? "
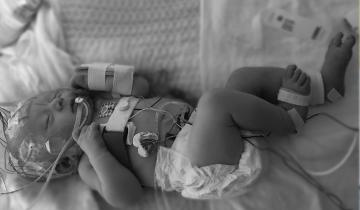
Receiving early diagnoses or high‐risk for CP classification is a parent priority. Alignment between parents and providers exists for International Classification of Function domains of body functions/structures and activity, but less for those of environment, personal, and participation.
My name is Nathalie Maitre, I work at Nationwide Children's Hospital. I'm a physician and a researcher

Owen is our third baby and after a healthy pregnancy and making it to 38 weeks, I thought we would coast into life with three kids and adapt to the beautiful chaos that is life outnumbered by little ones. Somewhere in between, I ended up watching as my newborn baby was packed up into a life-flight helicopter and whisked away before I even got a chance to hold him. I would do whatever it took to get to Owen at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, I would will him from hundreds of miles away to hang on, to fight long enough for me to get there – and then we could do “whatever it took” together.

Children with cerebral palsy experience brain damage around birth or before birth. So the language of the brain in other words, the way they will move, will be different from typical movements. So by looking at their movements, we will understand that there is something that is wrong in the brain.