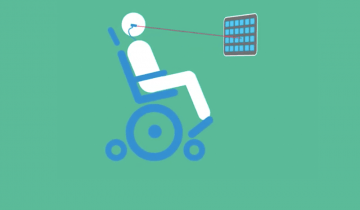
When a person is looking for a way to communicate in alternative ways, they need to find something that really works for them. They need to try to find a voice that sounds natural. They want to try to find a way to be efficient. They want to be able to communicate as normally as possible, even though they're not using their biological voice.