We studied how common pain was thought to be due to muscle spasticity in the legs or arms is in children/adolescents with CP.
Though the initial insult or injury to the brain that causes cerebral palsy is non-progressive, aging with cerebral palsy and lack of physical activity during critical periods of development can impact biologic and metabolic function for adults with cerebral palsy.
Drooling is an important problem for many individuals with CP and there are a number of interventions available to treat symptoms. If an individual with CP or their caregiver have concerns about drooling it is important to discuss with a health care provider. Care pathways such as the AACPDM pathway can be a starting point for shared decision making. In all cases, working together as a team is important in choosing the best alternative. Children and adults with CP may have trouble with drooling, or saliva management. In the medical world, drooling is referred to as sialorrhea. Saliva plays an important role in eating but also can interfere with airway clearance and breathing, as well as social participation. When drooling has this kind of impact it becomes important to consider intervention.
There are multiple factors that impact bone health, including birth weight, nutrition, medications for seizures and/or reflux, genetics, and physical activity. Targeted exercise to improve bone health in childhood can be sustained into adulthood, and childhood is the best time to promote bone health.
Our 3rd Virtual Town Hall featured experts from the Shirley Ryan Ability Lab and Northwestern University in Chicago. This multi-disciplinary panel discussion highlights the latest updates in care of children with #CerebralPalsy.

Our educational series kicked off with a panel of experts from the Weinberg Family CP Center at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City on Thursday, November 5th, 2020 at 6:30pm ET. This virtual event featured a multi-disciplinary panel discussion with Weinberg Family CP Center clinicians and researchers.

It is recommended that women start having mammography screenings starting at about the age of 40, and it becomes more difficult to obtain these services if you have a disability.

The findings of this article demonstrate the need for improved screening rates in women with CP, and highlight areas for improving their screening experience.
Cerebral palsy is an injury to the brain, but what we find is that it has a lot of effects on how you use your muscles.

For people with a physical disability, activity is a lifestyle. It's something that can start in physical therapy, but it really is something that has to be carried over into their everyday lives. What has happened over the years is we're understanding the importance of mobility.

Spasticity is a condition of muscles that is a velocity resistance to stretch. What that means to a child and to a parent is that if you move the limb slowly, you have a difference than if you move that limb fast. Spasticity restricts movement and it creates a break on the system. It's as if they're trying to move, but they're held back. By treating spasticity, you may improve the range of motion or the action of the movement.

Everybody tells stories, and that includes people who use communication systems. To ensure success and the ability to participate we need to make it as easy as possible. So that we can tell stories whenever we want, wherever we want, to whomever we want, and in a really easy way, so we can be successful.

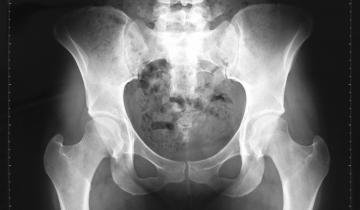
If your child has cerebral palsy, there's a good chance that he or she will have a hip x-ray at some point or they may even require regular hip x-rays. It is important for you to understand the different components of a hip x-ray. Your doctor will be looking at the hip joint itself as well how well the bones are growing.
Early interventions for CP should be based on the strongest possible scientific evidence for benefit and should have the smallest possible risk of harm. In the US, early intervention (EI) is a system of services available under the age of 3, to support infants and toddlers with developmental problems and their families as they interact with and care for their child.

In general, children with cerebral palsy will have stiffness around the hips and they tend to develop atypical hip positioning as a result of their spasticity. They will develop hip flexion contractures, abduction contractures, and they will have difficulty with seating as well as bathing and hygiene.