What is Chronic Drooling or Sialorrhea and Why is it Important?
This blog is sponsored by Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC, a distributor of XEOMIN (incobotulinumtoxinA).
Many children with cerebral palsy (CP) have difficulty controlling saliva. Drooling varies in severity and can be distressing for the children, families and caregivers. Chronic drooling is referred to as Sialorrhea and occurs as a result of limitations in a person’s ability to control and swallow oral secretions.
In children with CP, sialorrhea is usually the result of limited oromotor control as a result of muscle incoordination and sensory perception difficulties. Sialorrhea occurs in approximately 40% of children/youth with CP and can have significant medical and psychosocial impact.
Excessive drooling or Sialorrhea can cause constant damp soiled clothing, unpleasant odor, irritated, skin around the mouth and chin, skin and mouth infections, difficulties chewing, and interference with speech. There is also risk of social rejection and social isolation for children including the need for frequent clothing changes, damage to books, computers, toys and other equipment, as well as spray from the mouth while talking.
Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are a number of treatment strategies available that may help improve Sialorrhea. Goals of treatment can include: 1) improved control of secretions; 2) enhancement of a child’s ability to behaviorally manage secretions; and 3) reduction of saliva production or rerouting of salivary flow.
When possible, a multidisciplinary team approach is recommended, progressing from conservative to more invasive treatments until saliva control is improved and side effects, if present, are manageable. Treatment can include the following options:
- Optimizing conditions - Optimize positioning and consider other medical factors that may affect drooling. Consider whether medications being used for other conditions, such as epilepsy, are increasing drooling.
- Oromotor and orosensory strategies - Active and passive exercises as well as sensory applications are widely used by clinicians, although there is no agreement about the theoretical basis and effectiveness of these interventions.
- Behavioral strategies - Multiple types of behavioral procedures have been shown to be effective. Please consult with your clinician for more information and guidance.
-
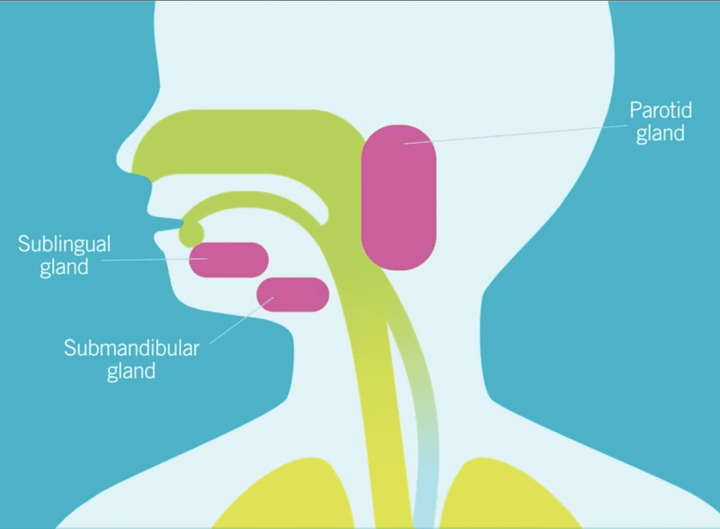
Intraglandular Botulinum toxin injections to the submandibular +/- parotid glands. XEOMIN® (incobotulinumtoxinA) is the first and only FDA-approved Botulinum Toxin for children (ages 2-17) with Chronic Sialorrhea*. It is often injected using ultrasound guidance for assistance. Consult with your doctor regarding your child’s eligibility and any possible side effects, which can be serious. Please review the Important Consumer Safety Information below for additional safety information. *Every person's experience will vary, and there are potential risks and side effects with intraglandular botulinum toxin injections. In clinical studies pediatric patients had significant and sustained reduction in saliva over 16 weeks. While XEOMIN can help improve chronic sialorrhea (drooling) symptoms it is important to talk to your healthcare provider to see what is right for you or your child.
-
Surgical intervention. Surgery is usually reserved for patients with profuse, persistent drooling that continues despite other treatments.
|
XEOMIN® (incobotulinumtoxinA) IMPORTANT CONSUMER SAFETY INFORMATION Read the Medication Guide before you start receiving XEOMIN® (Zeo-min) and each time XEOMIN is given to you as there may be new information. The risk information provided here is not comprehensive. To learn more:
|
||||||||||||
|
Uses XEOMIN is a prescription medicine:
It is not known if XEOMIN is safe and effective in children younger than:
|
||||||||||||
|
Warnings XEOMIN may cause serious side effects that can be life threatening. Get medical help right away if you have any of these problems any time (hours to weeks) after injection of XEOMIN:
These symptoms can happen hours to weeks after you receive an injection of XEOMIN. These problems could make it unsafe for you to drive a car or do other dangerous activities. Do not take XEOMIN if you: are allergic to XEOMIN or any of the ingredients in XEOMIN(see below for a list of ingredients in XEOMIN), had an allergic reaction to any other botulinum toxin product such as rimabotulinumtoxinB (Myobloc®), onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®, Botox® Cosmetic), or abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) or have a skin infection at the planned injection site. Before receiving XEOMIN, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Talk to your doctor before you take any new medicines after you receive XEOMIN. Using XEOMIN with certain other medicines may cause serious side effects. Do not start any new medicines until you have told your doctor that you have received XEOMIN in the past. Especially tell your doctor if you:
Ask your doctor if you are not sure if your medicine is one that is listed above. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. Possible Side Effects
XEOMIN can cause serious side effects including:
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with chronic sialorrhea include:
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in children 2 to 17 years of age with chronic sialorrhea include:
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with upper limb spasticity include:
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in children 2 to 17 years of age with upper limb spasticity include:
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with cervical dystonia include:
The most common side effects of XEOMIN in adults with blepharospasm include:
These are not all the possible side effects of XEOMIN. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||||||||||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of XEOMIN Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about XEOMIN that is written for health professionals. |
||||||||||||
|
Active Ingredient: botulinum toxin type A Inactive Ingredients: human albumin and sucrose |
Copyright © 2020 Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC. All rights reserved. MERZ, the MERZ logo, and XEOMIN are registered trademarks of Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA. Botox, Dysport and Myobloc are registered trademarks of their respective owners.






